Local journalists from China's three provinces reflect on 2024 and look into 2025
Insights from north, east, and northwest China
In 2024, I had the privilege of meeting many local journalists from across China. Many of them have spent over a decade in a specific province or region, giving them a far deeper understanding of local affairs. I’ve always hoped to share some of their observations and insights with you.
Over the past week, I had the opportunity to speak with three of these local journalists of Xinhua from north China's Hebei Province, east China's Jiangsu Province, and northwest China's Gansu Province, and asked them the same three key questions as follows:
1. What are some of the standout achievements in your province in 2024?
2. What are the most anticipated developments in your province for 2025?
3. What are the biggest challenges your province will face in 2025?
Alongside their responses, I’ve also added some of my own observations based on what I’ve learned about these provinces. While these journalists' views do not represent the position of Xinhua, I personally find their insights enlightening and valuable, particularly for those seeking a broader perspective on the country.
Hebei Province
Population (2023): 73.93 million
GDP (2023): 4.39 trillion yuan (about 600 billion U.S. dollars)
Seat: Shijiazhuang
Journalist: Yue Wenting, economic journalist based in Hebei
1. What are some of the standout achievements in Hebei Province in 2024?
Yue: Hebei is a traditional resource-rich and energy-intensive province. It has made new breakthroughs in promoting comprehensive green transformation. The installed capacity of wind and solar power in Hebei has exceeded 100 million kilowatts, accounting for more than 60 percent of the total installed capacity, ranking among the top in the country.
Moreover, according to the China Comprehensive Computing Power Index (2024) published by the China Academy of Information and Communications Technology, Hebei ranks first in the country for comprehensive computing power. Within the province, the cities of Langfang and Zhangjiakou rank first and second, respectively, in the computing power index at the municipal level.
In addition, the area has entered a phase of large-scale development while also relieving Beijing of functions non-essential to its role as China's capital.
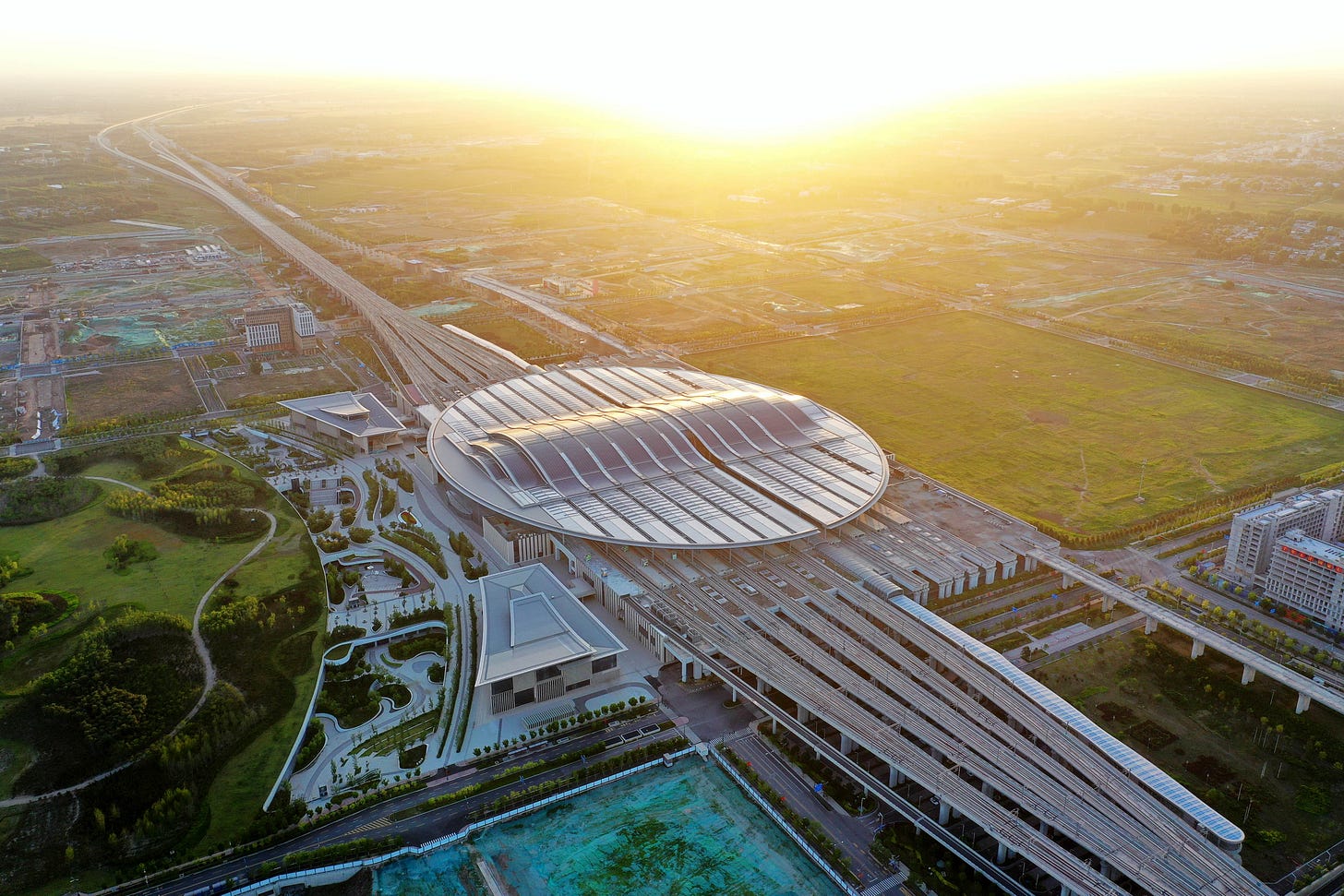
On Oct. 14, 2024, the office building of China Satellite Network Group Co., Ltd. in the Xiong'an New Area was officially put into use, marking the full relocation of the first centrally administered state-owned enterprise to settle in the region.
Nearly 300 centrally administered SOEs have set up offices in Xiong'an, including China Sinochem and China Huaneng Group. Construction is also speeding up for Xiong'an campuses of universities such as Beijing Jiaotong University, along with the Xiong'an branch of Peking University People's Hospital.
This aerial photo taken on June 2, 2023 shows the Xiong'an Railway Station in Xiong'an New Area, north China's Hebei Province.
2. What are the most anticipated developments in Hebei Province for 2025?
Yue: In recent years, Hebei has placed a strong emphasis on the development of industrial clusters, and has successfully established 107 key specialized industrial clusters. By the end of 2023, the total revenue generated by these clusters surpassed 4 trillion yuan, creating a unique landscape where every county in the province hosts its own industrial cluster.
According to the Hebei provincial government, by 2025, it aims to establish five industrial internet platforms dedicated to "共享智造 shared smart manufacturing," cultivate 10 leading "shared" enterprises, and set up 15 "shared" factories or workshops to this end.
The production model of "shared smart manufacturing," rooted in the sharing economy, seeks to optimize resource allocation and enhance productivity. It is expected to elevate Hebei's industrial clusters, fostering efficient and coordinated growth.
I have noticed that the cashmere industry in Qinghe, known as the “Cashmere Capital,” is catering to customers’ personalized needs through shared workshops. Similarly, the shared robot factories in Tangshan are enabling enterprises to share resources, reduce costs, and boost efficiency.
In 2025, more "shared" factories and workshops are expected to emerge across Hebei, and I look forward to reporting on them.
3. What are the biggest challenges Hebei Province will face in 2025?
Yue: Hebei is a major steel-producing province. In 2024, during my interviews with several steel enterprises in the province, it was evident that the steel industry has faced persistent pressure in recent years. Industry insiders have noted that the situation will become even more difficult by 2025, with some companies potentially struggling to survive. Similar challenges are also affecting other traditional sectors, such as apparel and chemicals.
As mentioned, Hebei needs to address the pressure of transforming its traditional industries. Sectors like steel and chemicals make up a large proportion of the province's economy, and urgently need to upgrade to more advanced, intelligent, and environmentally sustainable models.
Moreover, while Hebei has made significant progress in strengthening its innovation capabilities in recent years, there is still a noticeable gap compared to more developed regions. The province must further boost R&D investment, enhance innovation platforms, foster and scale up innovative enterprises, improve independent innovation capacity, break through key core technologies, and accelerate the conversion of scientific research results into industrial applications.
Context (added by editor):
In recent years, Hebei Province has been dedicated to three major events, namely the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics, the construction of the Xiong'an New Area, and the coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, also known as "Jing-Jin-Ji." 2024 marked the 10th anniversary of the launch of this regional coordinated development as a major national strategy.
Jiangsu Province
Population (2023): 85.26 million
GDP (2023): 12.82 trillion yuan
Seat: Nanjing
Journalist: Yang Shaogong, economic journalist based in Jiangsu
1. What are some of the standout achievements in Jiangsu Province in 2024?
Yang: The most remarkable achievement in Jiangsu has been its success in stabilizing economic growth, which has played a crucial role in helping the country meet its national economic objectives.
This is clearly reflected in the statistics. In the first three quarters, Jiangsu’s Gross Regional Product (GRP) reached 9.77 trillion yuan, marking a year-on-year growth of 5.7 percent, which is 0.9 percentage points higher than the national average. This growth rate was the highest among major economic provinces.
High-tech industries now account for 50.8 percent of the province's industrial output above a designated size. Besides, foreign direct investment amounted to 16.99 billion U.S. dollars, maintaining Jiangsu’s position as the top recipient in the country.
A defining feature of Jiangsu’s development is the deep integration of technological and industrial innovation, setting it apart from other regions in China. With its large and high-quality manufacturing sector, the province has a strong reliance on technological advancements and offers a rich environment for the application of new technologies.
Moreover, Jiangsu has achieved a historic milestone in its agricultural production, which is of great significance as it supports the province’s economic resilience and sustainable growth.
This year, the province’s grain output reached 76.2 billion jin (approximately 38.1 billion kilograms or 84 billion pounds), setting a new record and maintaining a steady output above 70 billion jin for 11 consecutive years. This stable production is expected to continue at this level in the coming year, ensuring food security and providing a solid foundation for Jiangsu’s consistent development.
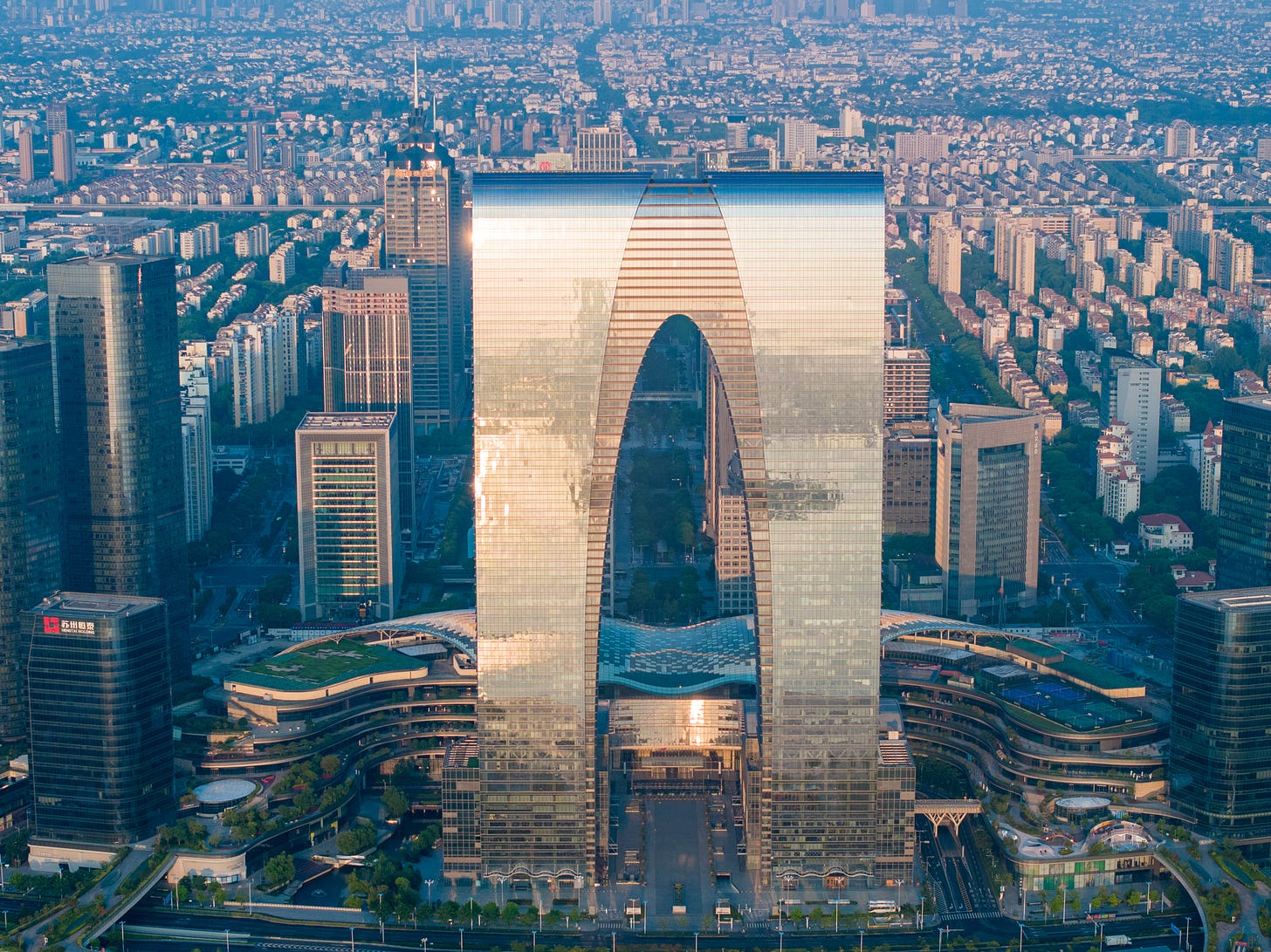
An aerial drone photo taken on Aug. 30, 2024 shows "the Gate of the Orient," a landmark complex at the Suzhou Industrial Park in Suzhou, east China's Jiangsu Province.
2. What are the most anticipated developments in Jiangsu Province for 2025?
Yang: Several developments in Jiangsu for 2025 are highly anticipated. Notably, the province will begin to progressively relax its household registration (hukou) restrictions, which is closely in line with the objectives set out in the third plenum of the 20th Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee to improve urban-rural integration and social security mechanisms. The reform of the hukou system is vital, as it allows for the free movement of people and other resources, thereby unlocking greater economic vitality and providing tangible benefits and a stronger sense of well-being to those migrating to urban areas.
The completion of five new cross-river passageways in Jiangsu next year is of great importance. These passageways are crucial because Jiangsu is divided by the Yangtze River into two distinct regions: the northern and southern parts of the province.
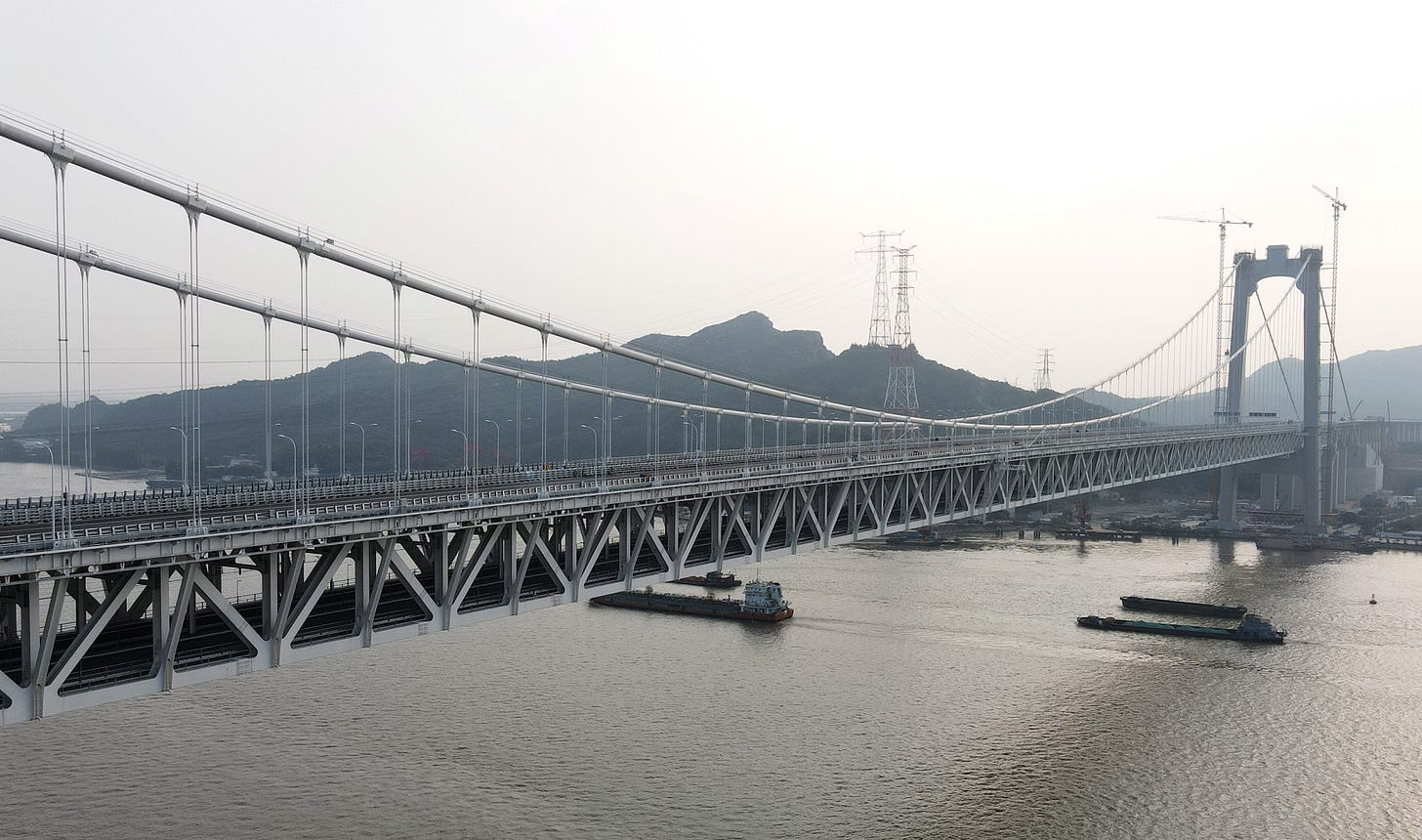
From the earliest Jiangyin Bridge on the Beijing-Shanghai Expressway to the more recent Wufengshan Yangtze River Bridge, which integrates both road and rail, all existing bridges have approached capacity very quickly. The construction of these new links is therefore a highly anticipated and critical development for Jiangsu’s ongoing growth and improved connectivity, both within the province and with the rest of the nation.
Aerial photo taken on Oct. 13, 2020 shows Wufengshan Yangtze River Bridge in east China's Jiangsu Province.
Jiangsu has the highest density of high-speed rail in China, yet its network continues to expand. Over the next three years, the province plans to add five more high-speed rail lines. This ongoing development is driven by the need to meet growing demand for efficient, high-quality transportation and to support future economic and technological growth, particularly in county-level cities.
Without convenient high-speed rail access, many research professionals are hesitant to relocate to these areas. Recognizing the importance of attracting talent to support its thriving county-level economies, Jiangsu is actively addressing this challenge through its transportation expansion.
3. What are the biggest challenges Jiangsu Province will face in 2025?
Yang: The most significant challenge remains sustaining economic growth while simultaneously improving the sense of well-being among the population. As previously mentioned, a fundamental shift is needed in the government’s approach to investment. The focus should move from relying heavily on attracting investment for large-scale projects to using public funds to build high-quality infrastructure in areas such as elderly care, healthcare, and education.
By addressing the basic concerns of residents, Jiangsu can truly enhance their quality of life, thereby unleashing greater consumer spending power. This challenge is not unique to Jiangsu; it is a nationwide issue.
Context (added by editor): Jiangsu has been at the forefront of major reforms and initiatives, setting a benchmark for many other provinces. It has served as a pioneering region for the Beautiful China Initiative and has set a distinguished example in advancing Chinese modernization, while also in implementing the reform objectives articulated at the third plenum of the 20th CPC Central Committee, such as building a high-standard socialist market economy, promoting high-quality economic development, and supporting all-round innovation.
Gansu Province
Population (2023): 24.65 million
GDP (2023): 1.19 trillion yuan
Seat: Lanzhou
Journalist: Zhang Yujie, economic journalist based in Gansu
1. What are some of the standout achievements in Gansu Province in 2024?
Zhang: Gansu, as a representative inland province in northwest China, faces challenges in terms of economic and social development. The province's industrial sector remains largely centered on primary processing, with industries characterized by short value chains, low added value, and significant development pressures.
Despite these challenges, Gansu possesses distinct advantages, including abundant mineral resources, a solid industrial base, and a robust scientific and technological infrastructure. Gansu is the first province in northwest China to establish modern industry in the late 19th century. Key institutions such as the Northwest Institute of Eco-Environment and Resources (NIEER) of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Lanzhou Institute of Physics of China Academy of Space Technology, and Lanzhou University further strengthened the province’s capacity for innovation and development.
In 2024, the Lanzhou Petrochemical Company, a regional subsidiary of China's largest natural gas producer and supplier CNPC, passed an internal review of a planned investment of over 24 billion yuan for the million-ton ethylene transformation project. The total investment for this project even exceeds the company's existing fixed assets.
In recent years, Gansu made significant strides in advancing new industrialization, which had a profound impact on its economic development. In the first three quarters of 2024, Gansu's GDP growth rate increased by 6 percent year-on-year, surpassing the national growth rate by 1.2 percentage points, ranking second in the country. This marks the 11th consecutive quarter that Gansu's GDP growth has outpaced the national average.
2. What are the most anticipated developments in Gansu Province for 2025?
Zhang: In 2025, I have high expectations for technological innovation in Gansu. I hope the province could endeavor to translate more scientific research into production benefits by taking full advantage of the research institutes and platforms in the region such as the Lanzhou-Baiyin Science and Technology Innovation Reform Experimental Zone.
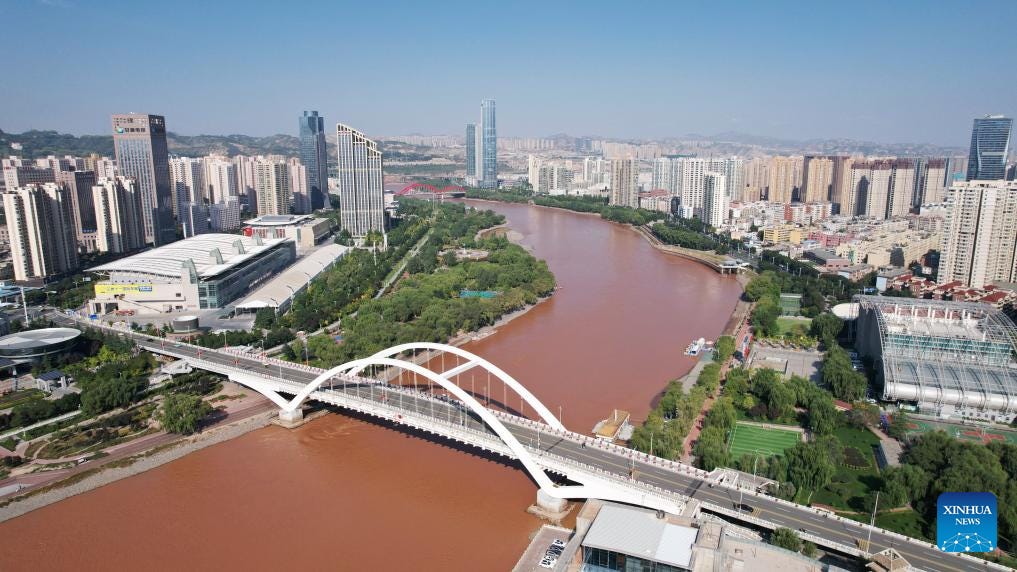
An aerial drone photo taken on Sept. 23, 2024 shows a view along the Yellow River in Lanzhou, northwest China's Gansu Province.
I also look forward to Gansu making further progress in the ecological protection and high-quality development of the Yellow River Basin.
Despite accounting for only 2 percent of the country's total water runoff, the Yellow River, revered as China's "Mother River" and a cradle of Chinese civilization, plays a vital role in ensuring water security for 12 percent of the population and 17 percent of the country’s farmland. It also serves as the primary water source for more than 50 large and medium-sized cities.
Gansu is a key water conservation and recharge area in the upper reaches of the Yellow River. About 60 percent of the river's water comes from the section above its capital, Lanzhou, and nearly one-fifth of the Yellow River flows through Gansu, spanning over 900 kilometers.
Since 2021, Gansu has effectively improved the water conservation and recharge capacity of the upper reaches through an integrated protection and restoration project for its mountains, waters, forests, lakes, grasslands and sand resources in the upper Yellow River Basin.
However, some deep-rooted contradictions remain unresolved. For instance, the overall scarcity of water resources in the basin contrasts with the rising demand for water due to economic and social development.
I hope the《中共甘肃省委关于全面推动黄河流域生态保护和高质量发展的决定(讨论稿)》Decision on Fully Promoting Ecological Protection and High-Quality Development of the Yellow River Basin (Draft for Discussion), approved at the Seventh Plenary Session of the 14th Committee of the Gansu Provincial Committee of the CPC on Dec. 21, will help resolve these deeper contradictions. This will not only continue to improve the river’s ecological environment but also better drive economic development along the Yellow River, reducing regional disparities and promoting high-quality growth.
3. What are the biggest challenges Gansu Province will face in 2025?
Zhang: Gansu faces significant challenges in narrowing the gap with more developed regions. China’s vast geography is marked by growing regional disparities, and while the western regions, Gansu included, are vital for strategic and ecological security, they remain economically underdeveloped. Gansu, in particular, struggles with attracting talent and investment, which hinders its ability to catch up with more prosperous areas. If these regional disparities, especially in the economic sector, continue to widen, it could pose long-term challenges for sustainable development in the region.
A major obstacle for Gansu is its reliance on traditional industries as the primary drivers of economic growth. The province remains heavily dependent on mineral resources and petrochemicals, with limited progress in cultivating emerging industries or fostering innovation.
Context (added by editor):
Located in the northwest of the province, on the edge of the Taklamakan Desert, Dunhuang is the region's most renowned historical city. To the southeast of Dunhuang lies the Mogao Grottoes, home to the world’s largest, most richly adorned, and longest-used treasure trove of Buddhist art. In 1987, the site was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List.
Picture from Shanghai Daily: Murals of Cave No. 112, Middle Tang Dynasty (781-847)
For over two thousand years, Gansu has held a strategic position along the Silk Road, serving as a crucial link between China and Central Asia. Traders and travelers journeying in and out of China have historically passed through the narrow 1,200-kilometer strip of land in central Gansu, dotted with oasis towns and military outposts. This vital route, known as the 河西走廊 Hexi Corridor, has long been one of the most important passages of the ancient Silk Road.
A camel caravan is seen at sunset in a desert in Zhangye, northwest China's Gansu Province, June 14, 2015.